Key Takeaways
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Penumbra Paths | Partial shadow areas where only part of the light is blocked. |
| Eclipses | Penumbra paths form during lunar and solar eclipses. |
| Shadow Geometry | Penumbra paths shape our understanding of light diffusion. |
| Practical Applications | Important in photography, solar panels, and space research. |
| Artistic Impact | Penumbra paths influence light and shadow in visual arts. |
Penumbra paths might sound like a scientific term, but they show up more often than you think! These partial shadows occur when light from a source is blocked only partially by an object. This simple yet important concept can be seen in many places, from celestial events like solar and lunar eclipses to how we capture light in photography. In this article, we’ll uncover how penumbra paths work and why they matter in different fields.
Basic Understanding and Definition of Penumbra Paths
What are penumbra paths in shadow theory?
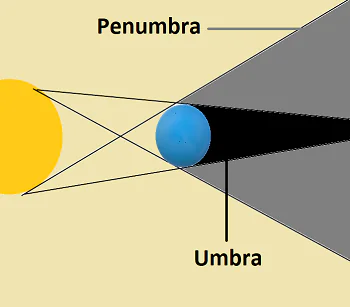
A penumbra path is the area of partial shadow that occurs when an object blocks some, but not all, of the light coming from a source. This happens when the light is diffused in such a way that only part of the area behind the object is in full darkness (the umbra) and the rest is partially lit. The term penumbra comes from Latin, meaning “almost shadow.”
| Penumbra Path Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition | Area of partial shadow created by the blockage of light. |
| Visual Effect | Creates softer, diffused shadows. |
Understanding the geometry of penumbra paths
The geometry of penumbra paths can be visualized as the transition zone between full light (illumination) and full darkness (shadow). This is affected by the relative positions of the light source, object, and observer. For example, during an eclipse, the penumbra path forms the outermost edge of the shadow, blending from light to dark.
- The light source could be a star like the Sun or artificial lighting.
- The object might be a planet, moon, or an everyday item.
How do penumbra paths affect light diffusion?
Penumbra paths play a major role in how light is spread across a surface. They create a gradual fading from bright light to darkness, resulting in softer edges around shadows. This light diffusion can affect how we perceive objects in both natural and artificial lighting.
- Photographers use this knowledge to create balanced, soft lighting for portraits or landscapes.
- Interior designers incorporate this idea to soften the harshness of artificial light.
The relationship between penumbra paths and umbra regions
The penumbra is distinct from the umbra, which is the area of full shadow where no light can reach. The umbra is dark and sharp, while the penumbra provides a gradient transition from light to dark. Think of the penumbra as the blurry edges around the darkness cast by an object.
| Shadow Type | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Penumbra | Partial shadow, light transition. |
| Umbra | Full shadow, no light passes through. |
Penumbra Paths in Natural Phenomena
Penumbra paths in the context of lunar eclipses
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth casts its shadow on the Moon, and the penumbra path is the outermost edge of that shadow. When the Moon passes through the penumbra, the shadowed area looks dimmer than usual but still visible. Observing this penumbral shadow gives us insight into the alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
- Eclipses often spark curiosity about how light travels and how we experience these celestial events.
Penumbra paths and their impact on solar observations
During a solar eclipse, the Moon casts a shadow over the Earth, creating a penumbra path on the surface. The penumbra is where observers on Earth will experience a partial eclipse. The closer you are to the center of the penumbra, the more the Sun is obscured.
| Event Type | Effect of Penumbra |
|---|---|
| Solar Eclipse | Partial obscuration of the Sun’s light. |
| Lunar Eclipse | A dimming effect on the Moon. |
Visualizing penumbra paths in astronomical events
Astronomers use advanced telescopes and satellites to visualize penumbra paths during eclipses. These instruments help track the movement of shadows across the Earth’s surface, which is essential for studying the geometry of celestial bodies.
- Tools like solar observatories help us understand these phenomena in greater detail.
Penumbra paths and the physics behind eclipses
The physics of an eclipse involves light bending and diffraction, and the penumbra path is where these effects are most noticeable. When the Sun‘s light is partially blocked, the intensity of the light changes, causing the shadow to become softer around the edges.
- Diffraction happens when light bends around objects, influencing how we perceive the penumbra.
How do penumbra paths vary with the position of the sun?
The size and shape of penumbra paths are affected by the angle at which the Sun’s rays strike the object. During different times of the year, the Sun’s position shifts, altering the location of the penumbra during eclipses or other phenomena.
- The altitude and azimuth of the Sun affect how penumbra paths are formed across the sky.
Analyzing penumbra paths during partial solar eclipses
During a partial solar eclipse, only the outer part of the Sun is obscured by the Moon. This creates a penumbra path on Earth where the Sun appears as a crescent. Scientists track this path to study the mechanics of these celestial events.
- Tracking penumbra paths during a partial solar eclipse can reveal important details about the alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
Can penumbra paths be seen with the naked eye during an eclipse?
Yes, penumbra paths can be seen with the naked eye, but they are subtle. The light changes gradually, making the transition from sunlight to shadow smooth. During a solar eclipse, observers in the penumbra zone may notice a slight dimming, but the full effect requires careful observation.
Penumbra Paths in Scientific and Practical Applications
How to calculate penumbra paths during a solar eclipse
Scientists use complex mathematics to calculate the precise size and location of the penumbra during a solar eclipse. By studying the geometry of the Earth, Moon, and Sun, they predict where the penumbra will fall.
| Calculation Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Distance | Between Earth, Moon, and Sun. |
| Geometry | Of the light source and obstruction. |
Penumbra paths and their role in environmental lighting
In architecture and lighting design, understanding penumbra paths helps create well-lit spaces with soft, diffused shadows. This is especially useful in interior design, where lighting can affect mood and atmosphere.
- Using penumbra effects, designers create lighting systems that reduce harsh shadows while still maintaining visibility.
Penumbra paths and their interaction with surrounding objects
When an object partially blocks light, the resulting penumbra path can interact with nearby objects. This creates softer shadows, especially when the light source is far away. The shadow’s intensity and edge sharpness are influenced by how close objects are to the light.
- In photography, understanding how the penumbra interacts with objects helps photographers control the mood of their images.
How are penumbra paths used in the study of celestial bodies?
Astronomers study penumbra paths during eclipses to better understand the distances between celestial bodies. By observing how shadows move across the Earth, scientists can refine their knowledge of planetary motion.
| Study Area | Contribution of Penumbra |
|---|---|
| Astronomy | Provides data on celestial body distances. |
Penumbra paths and their influence on solar panel efficiency
Solar panels are designed to capture the Sun’s energy. Understanding penumbra paths is crucial for determining the ideal placement of solar panels. Shadows, even partial, can affect the panel’s ability to collect energy.
Penumbra Paths in Artistic and Creative Contexts
Penumbra paths in artistic representations of light and shadow
Throughout history, artists have used penumbra paths to create more realistic lighting effects in their artwork. Whether in painting or cinematography, the blending of light and shadow plays a significant role in how viewers perceive depth and contrast.
- Caravaggio, for example, mastered the use of light and shadow to create dramatic effects in his paintings.
The significance of penumbra paths in light source behavior
Understanding how light behaves in penumbra paths helps artists and designers control how shadows are cast in their works. By experimenting with light sources and the distance between the subject and the light, artists can manipulate shadows to convey mood or emphasize details.
Penumbra paths and the science of shadow casting
The science of how shadows are cast—especially the role of penumbra paths—is important in both photography and cinematography. In motion pictures, lighting is key to creating mood and guiding audience focus.
Advanced Applications and Insights
Penumbra paths in the formation of space phenomena
In space research, penumbra paths are important when studying the behavior of light and shadow on planets, moons, and other celestial bodies. By observing how light behaves during an eclipse or transit, scientists can gain insights into planetary atmospheres.
Conclusion
Penumbra paths are more than just shadows; they’re windows into the complex behavior of light. Whether it’s the delicate edges of a solar eclipse or the soft shadows in a photograph, understanding penumbra paths allows us to better understand how light shapes our world, from natural phenomena to the world of art and design.